1 中国计量大学 光学与电子科技学院,杭州 310018
2 中国工程物理研究院 上海激光等离子体研究所,上海 201899
3 上海理工大学 光子芯片研究院,上海 200093
4 上海理工大学 光电信息与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
高效、高平均功率固体纳秒脉冲激光器在光电对抗、激光雷达、材料改性、激光加工等诸多领域发挥着越来越重要的作用,然而目前大多数纳秒级高平均功率激光器采用Yb:YAG或掺Nd材料作为增益介质,材料的高饱和通量或低储能密度会导致激光器放大链路复杂,体积庞大。研究比较了一种更适合作为高平均功率、高脉冲能量激光器增益介质的无序石榴石晶体Yb:CNGG,研究了有源反射镜结构中Yb:CNGG的多程增益特性,分析了放大过程并建立了多程放大模型,在一定的泵浦条件下优化了晶体参数以实现更好的储能。开展了双程放大实验,在15 kW/cm2的泵浦功率密度下得到了1.53倍的增益。对比Yb:CNGG晶体与Yb:YAG晶体的多程放大能力,在相同的晶体参数和泵浦条件下,在入射能量1 mJ时Yb:CNGG可实现2.11 J的脉冲能量输出,优于Yb:YAG晶体1.41 J的能量输出。
Yb:CNGG 激光放大器 多程放大 有源反射镜 激光二极管 Yb: CNGG laser amplifier multi-pass amplification active mirror laser diode 强激光与粒子束
2023, 35(3): 031003
1 中国计量大学光学与电子科技学院,浙江 杭州 310018
2 中国工程物理研究院上海激光等离子体研究所,上海 201800
定量分析光纤阵列位移及指向扰动偏差对合束激光光束质量因子M2的影响规律是实现合束激光光束质量有效控制的前提。根据衍射积分推导了紧凑型光谱组束系统中光纤阵列存在不同位移、指向扰动时合束激光的远场光强分布,利用Heisenberg不确定性原理推导出了合束激光光束质量因子M2的表达式。在恒定的子束数目下,分析了单路/多路光束分别存在位移、指向扰动偏差时合束激光光束质量因子M2的变化情况,并在一定的随机位移、指向扰动偏差下对不同子束数量的合束激光的光束质量因子M2进行了误差分析。结果显示:合束激光光束质量因子M2对沿光纤端面水平(x轴)方向的扰动量最为敏感,需要控制在微米量级;确定了光纤阵列的不同扰动量与合束激光光束质量因子M2之间的定量关系,给出了光纤阵列位移、指向精度控制要求;当参与合束的子束数量超过23束时,在特定的随机扰动量下,合束激光的光束质量因子M2的统计均值分别趋向各自的稳定值1.37、1.34、1.25,而标准差分别趋于0.05、0.06、0.04。
光纤光学 光纤阵列 光束质量 光谱组束 紧凑型组束系统
1 电子科技大学物理学院, 四川 成都 611731
2 中国工程物理研究院上海激光等离子体研究所, 上海 201800
高效宽带的三次谐波转换是激光惯性约束聚变驱动器的关键技术之一。超辐射光的宽带特性以及宽、窄带和频方案为这一研究提供了新的实现途径。本文基于超辐射光特性,建立了其三倍频过程数值计算模型,并分析了时间高相干基频光与超辐射倍频光和频的效率和光谱特性演化。与超辐射光直接三倍频相比,宽、窄和频方案能够有效地减小群速度失配对超辐射光三倍频效率的影响,可以将超辐射光三倍频效率提升至44%,输出三倍频带宽可达到1.9 THz,该结果可指导超辐射光三倍频系统的设计与相关实验研究。
非线性光学 超辐射光 非线性频率转换 群速度失配 中国激光
2021, 48(21): 2108001
红外与激光工程
2020, 49(12): 20201074
强激光与粒子束
2020, 32(11): 112009
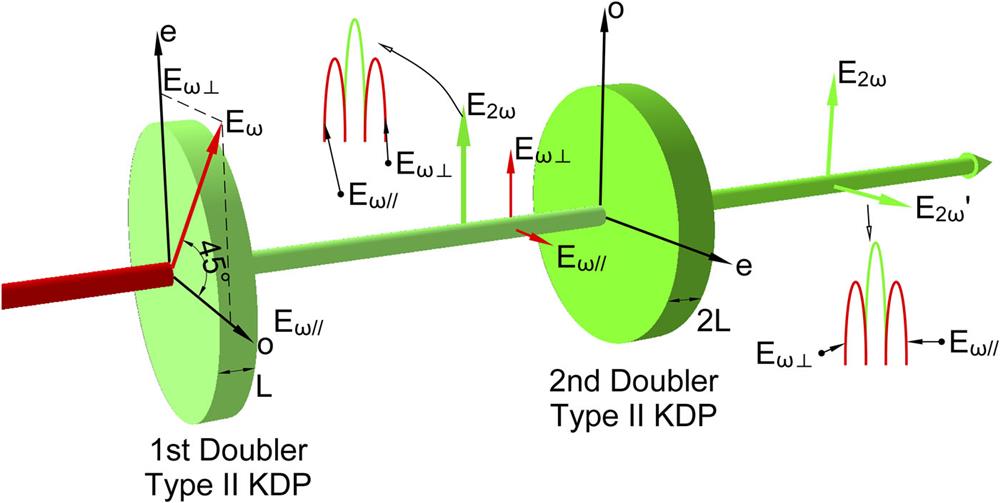
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Shanghai 201899, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
3 School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, China
The use of low-coherence light is expected to be one of the effective ways to suppress or even eliminate the laser–plasma instabilities that arise in attempts to achieve inertial confinement fusion. In this paper, a review of low-coherence high-power laser drivers and related key techniques is first presented. Work at typical low-coherence laser facilities, including Gekko XII, PHEBUS, Pharos III, and Kanal-2 is described. The many key techniques that are used in the research and development of low-coherence laser drivers are described and analyzed, including low-coherence source generation, amplification, harmonic conversion, and beam smoothing of low-coherence light. Then, recent progress achieved by our group in research on a broadband low-coherence laser driver is presented. During the development of our low-coherence high-power laser facility, we have proposed and implemented many key techniques for working with low-coherence light, including source generation, efficient amplification and propagation, harmonic conversion, beam smoothing, and precise beam control. Based on a series of technological breakthroughs, a kilojoule low-coherence laser driver named Kunwu with a coherence time of only 300 fs has been built, and the first round of physical experiments has been completed. This high-power laser facility provides not only a demonstration and verification platform for key techniques and system integration of a low-coherence laser driver, but also a new type of experimental platform for research into, for example, high-energy-density physics and, in particular, laser–plasma interactions.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2020, 5(6): 065201
强激光与粒子束
2020, 32(1): 011004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, Shanghai 201800, China
In high power laser facility for inertial confinement fusion research, final optics assembly (FOA) plays a critical role in the frequency conversion, beam focusing, color separation, beam sampling and debris shielding. The design and performance of FOA in SG-II Upgrade laser facility are mainly introduced here. Due to the limited space and short focal length, a coaxial aspheric wedged focus lens is designed and applied in the FOA configuration. Then the ghost image analysis, the focus characteristic analysis, the B integral control design and the optomechanical design are carried out in the FOA design phase. In order to ensure the FOA performance, two key technologies are developed including measurement and adjustment technique of the wedged focus lens and the stray light management technique based on ground glass. Experimental results show that the design specifications including laser fluence, frequency conversion efficiency and perforation efficiency of the focus spot have been achieved, which meet the requirements of physical experiments well.
final optics assembly high power laser facility inertial confinement fusion. High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(2): 02000e14
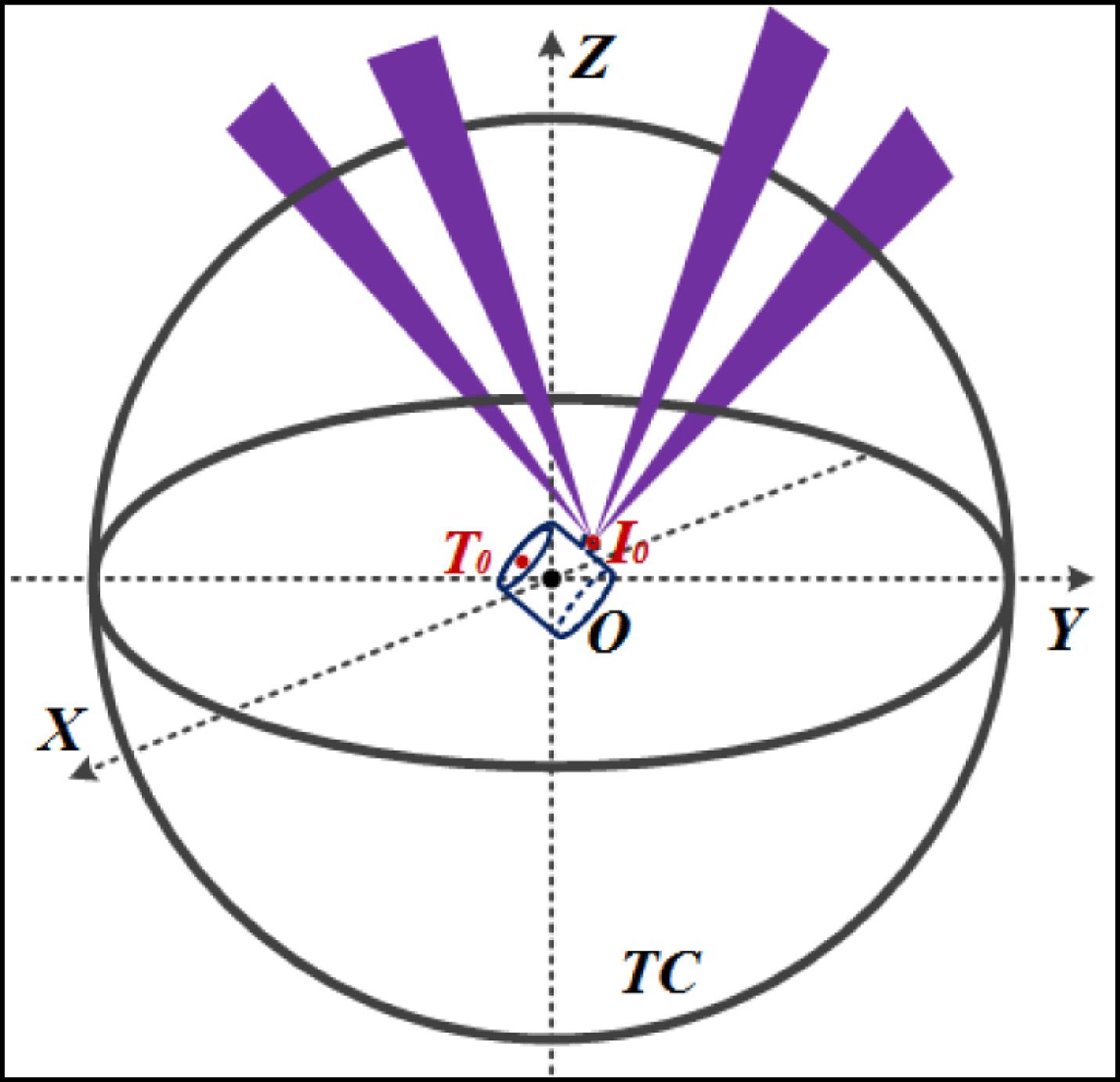
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Shanghai 201800, China
The Shen-Guang II Upgrade (SG-II-U) laser facility consists of eight high-power nanosecond laser beams and one short-pulse picosecond petawatt laser. It is designed for the study of inertial confinement fusion (ICF), especially for conducting fast ignition (FI) research in China and other basic science experiments. To perform FI successfully with hohlraum targets containing a golden cone, the long-pulse beam and cylindrical hohlraum as well as the short-pulse beam and cone target alignment must satisfy tight specifications (30 and $20~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ rms for each case). To explore new ICF ignition targets with six laser entrance holes (LEHs), a rotation sensor was adapted to meet the requirements of a three-dimensional target and correct beam alignment. In this paper, the strategy for aligning the nanosecond beam based on target alignment sensor (TAS) is introduced and improved to meet requirements of the picosecond lasers and the new six LEHs hohlraum targets in the SG-II-U facility. The expected performance of the alignment system is presented, and the alignment error is also discussed.
laser drivers petawatt lasers spherical hohlraum target alignment target area High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(1): 01000e10





